The Role of Nutrition in Eye Health: Foods for Better Vision
Introduction
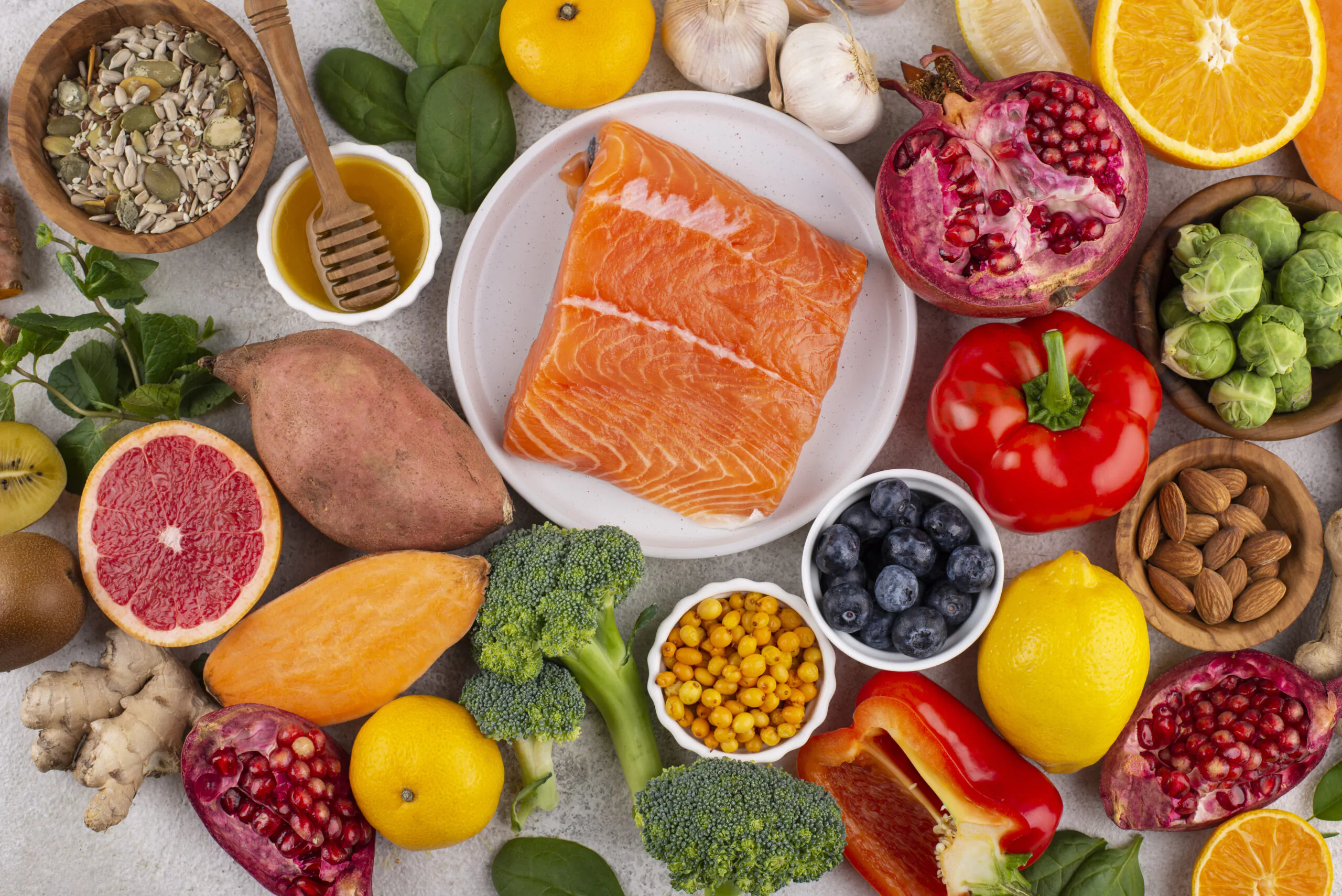
When it comes to maintaining healthy vision, nutrition plays a significant role. A well-balanced diet rich in certain nutrients can help support eye health and potentially reduce the risk of age-related eye conditions. In this blog, we will explore the essential nutrients and foods that can contribute to better vision and overall eye health.
- Vitamin A
Vitamin A is essential for good vision and overall eye health. It helps protect the cornea, the outermost layer of the eye, and is a component of rhodopsin, a pigment that aids in low-light vision. Foods rich in vitamin A include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, and other leafy greens. These foods are not only packed with vitamin A but also contain other beneficial antioxidants that support eye health.
- Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect the eyes from damage caused by free radicals. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of blood vessels in the eyes. Citrus fruits such as oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are excellent sources of vitamin C. Other sources include strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli. Including these foods in your diet can help reduce the risk of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
- Vitamin E
Vitamin E is another powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells in the eyes from oxidative stress. It works in conjunction with other antioxidants to maintain healthy eye tissues. Foods rich in vitamin E include nuts (such as almonds and hazelnuts), seeds (such as sunflower seeds), spinach, and fortified cereals. Adding these foods to your diet can contribute to the overall health of your eyes.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that provide numerous health benefits, including supporting eye health. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid, is found in high concentrations in the retina of the eye and is crucial for its proper function. Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. For those who don’t consume fish, plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts can provide alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which the body can convert to DHA to a certain extent.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin Lutein and zeaxanthin are antioxidants known as carotenoids that accumulate in the retina and lens of the eye. They help filter harmful high-energy blue light and protect against oxidative damage. Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich sources of these carotenoids. Other sources include broccoli, peas, corn, and eggs. Regular consumption of these foods can contribute to maintaining healthy vision and reducing the risk of AMD and cataracts.
- Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that plays a vital role in eye health. It helps transport vitamin A from the liver to the retina, where it produces melanin, a protective pigment. Zinc also supports the health of the cells in the eyes. Oysters contain one of the highest levels of zinc, but other sources include lean meats, poultry, beans, and nuts. Adding zinc-rich foods to your diet can help maintain proper eye function.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods
In addition to the specific nutrients mentioned above, a diet rich in antioxidants is beneficial for overall eye health. Antioxidants help protect the eyes from oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Colorful fruits and vegetables such as berries, oranges, grapes, and bell peppers are excellent sources of antioxidants. Additionally, green tea and dark chocolate (in moderation) also contain antioxidants that promote eye health.
Conclusion
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining healthy vision and reducing the risk of age-related eye conditions. By incorporating foods rich in vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, lutein, zeaxanthin, zinc, and antioxidants into your diet, you can support the health of your eyes. Remember to maintain a well-balanced diet, including a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, to provide your eyes with the nutrients they need to function optimally. Combined with regular eye exams and healthy lifestyle habits, a nutritious diet can contribute to better vision and long-term eye health.